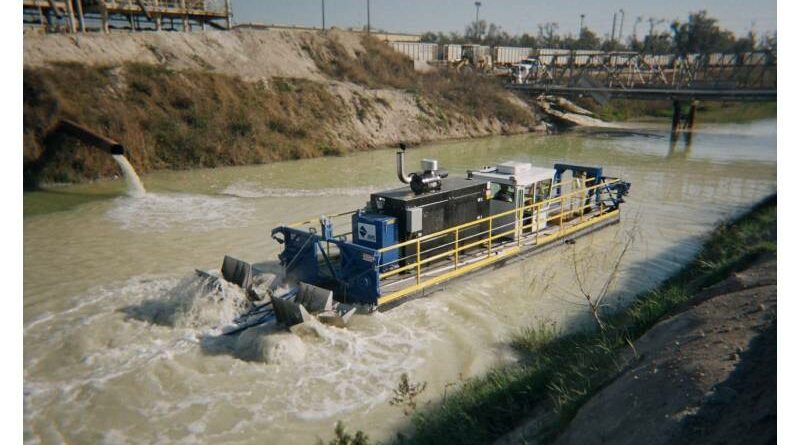
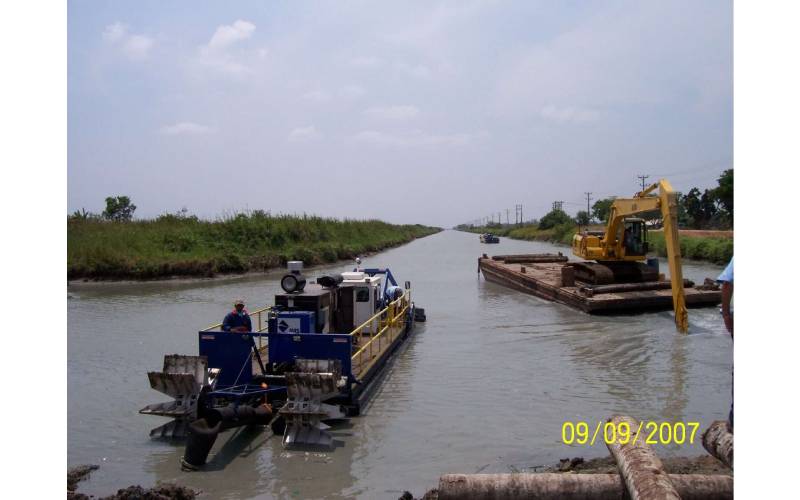
The Importance of Regular Dredging for Long-Term Lake Sustainability
Lakes are valuable natural resources that provide ecosystems for wildlife, recreational opportunities for communities, and essential water storage. However, without proper management, these water bodies can degrade over time, leading to ecological imbalance, reduced usability, and even complete loss of the lake’s functionality. One critical maintenance process that ensures the health and longevity of lakes is dredging. In particular, a canal dredge plays an instrumental role in sustaining both lakes and their connected waterways. This article delves into the importance of regular dredging for long-term lake sustainability, explaining the process, its benefits, and how a canal dredge contributes to this essential task.
Understanding Dredging And Canal Dredges
Dredging involves the removal of sediment, debris, and other materials that accumulate on the bottom of a water body. Over time, sediments from erosion, decaying organic matter, and human activities settle at the bottom, reducing the depth and usability of lakes. A canal dredge is a specialized piece of equipment used to remove these sediments, particularly in narrow or confined waterways connected to lakes, such as canals. Canal dredge are designed to navigate restricted areas and perform precise sediment removal, making them invaluable in lake management. By ensuring proper water flow and sediment removal, these machines help maintain the ecological and functional balance of the lake system.

Causes Of Sedimentation In Lakes
- Erosion: Natural erosion from nearby hills and riverbanks contributes large amounts of soil and debris to lakes.
- Runoff: Agricultural and urban runoff often carries sediments, fertilizers, and pollutants into lakes, exacerbating sedimentation.
- Human Activities: Construction, boating, and other recreational activities can disturb the lake’s ecosystem, leading to sediment buildup.
- Decaying Organic Matter: Plants and aquatic organisms that die and decompose contribute to organic sediments.
Key Benefits Of Regular Dredging
1. Improved Water Quality
Excess sediment can lead to murky water, reduced sunlight penetration, and lower oxygen levels. This impacts aquatic plants and fish populations. Dredging removes these sediments, improving water clarity and overall quality.
2. Prevention of Algal Blooms
Nutrient-rich sediments, particularly those containing phosphorus and nitrogen, fuel algal blooms. These blooms can deplete oxygen levels, harming aquatic life and creating unpleasant odors. Regular dredging removes nutrient-rich sediments, reducing the likelihood of algal blooms.
3. Enhanced Biodiversity
Sedimentation often disrupts habitats for aquatic species. By dredging and restoring the lake’s depth and quality, diverse species can thrive once again, promoting a balanced ecosystem.
4. Increased Lake Depth
Sedimentation reduces the lake’s depth over time, limiting its functionality for recreation, fishing, and navigation. Dredging restores depth, ensuring the lake remains usable for various purposes.
5. Flood Control
Sediment buildup can obstruct water flow, leading to increased flood risks during heavy rains. By maintaining clear pathways with a canal dredge, water can flow freely, reducing the likelihood of floods.
6. Extended Lifespan of Lakes
Unchecked sedimentation can lead to the eventual disappearance of a lake. Regular dredging prevents this, ensuring the lake remains a valuable resource for generations.
The Role Of Canal Dredges In Lake Sustainability
Canal dredges are uniquely suited to maintaining the intricate connections between lakes and their surrounding waterways. Here’s how they contribute:
1. Targeted Sediment Removal
Canal dredges can focus on specific areas, such as narrow canals or lake inlets, where sedimentation is most severe. This precision ensures efficient sediment management.
2. Navigation Maintenance
Connected canals often serve as transportation routes for boats and other vessels. Canal dredges keep these waterways navigable, supporting recreational and commercial activities.
3. Water Flow Management
Sediment buildup in canals can impede water flow, leading to stagnant areas prone to algal blooms and reduced oxygen levels. Canal dredges restore proper flow, improving overall lake health.
4. Protection of Infrastructure
Bridges, docks, and other infrastructure near lakes and canals can suffer damage from sediment buildup. Regular dredging with a canal dredge reduces this risk, protecting investments and ensuring safety.
The Process Of Dredging
The dredging process typically involves several steps:
- Survey and Assessment: Before dredging begins, experts assess the sediment’s composition, the lake’s depth, and areas of concern. This helps in planning an effective dredging strategy.
- Equipment Selection: Depending on the lake’s size and the type of sediment, appropriate dredging equipment, such as a canal dredge, is chosen.
- Sediment Removal: The dredge removes sediment, which is often transported to designated disposal or treatment areas.
- Site Restoration: After dredging, efforts are made to restore the site, ensuring minimal disruption to the ecosystem.
Environmental Considerations
While dredging is essential, it must be conducted responsibly to minimize environmental impact. Key considerations include:
- Timing: Avoiding dredging during spawning seasons or when sensitive species are present.
- Sediment Testing: Analyzing sediments for pollutants ensures safe disposal or treatment.
- Erosion Control: Implementing measures to prevent future sedimentation, such as planting vegetation along shorelines.
Strategies For Sustainable Lake Management
- Regular Monitoring: Conduct routine assessments to identify sedimentation trends and plan timely dredging.
- Community Involvement: Engage local communities in lake conservation efforts, including awareness campaigns and clean-up drives.
- Integrated Approaches: Combine dredging with other strategies, such as erosion control and pollution reduction, for holistic lake management.
- Investing in Advanced Equipment: Modern canal dredges with advanced technology can perform more efficient and environmentally friendly dredging.
Conclusion
Regular dredging, particularly with the use of specialized canal dredges, is a cornerstone of long-term lake sustainability. It not only preserves the ecological balance but also ensures that lakes remain functional and beneficial for communities and wildlife. By addressing sedimentation proactively and responsibly, we can protect these vital resources for future generations. Investing in regular dredging is not just about maintaining a water body; it’s about securing the myriad of benefits that lakes and their connected canals provide, from biodiversity and recreation to flood control and water quality. Prioritizing dredging as part of a comprehensive lake management strategy is essential for their long-term health and sustainability.