Unlocking Muscle Spasms: Causes, Relief, and Prevention Tips
Muscle spasms are sudden, involuntary contractions of one or more muscles. They can be painful and disruptive. Understanding the causes, finding relief, and learning prevention tips can help manage and reduce the occurrence of muscle spasms.
What Are Muscle Spasms?
Muscle spasms occur when a muscle contract involuntarily and does not relax. They can happen in any muscle but are most common in the legs, arms, abdomen, and back. Spasms can last from a few seconds to several minutes. Sometimes, they may recur multiple times before going away.
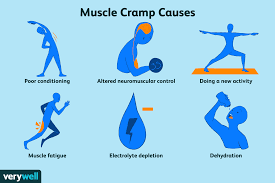
Common Causes of Muscle Spasms
Muscle spasms can result from various factors. Identifying the cause is the first step toward finding relief and preventing future episodes.
Dehydration
Dehydration is a leading cause of muscle spasms. When the body lacks sufficient fluids, muscles are more prone to cramping. This is especially common during intense physical activity or in hot weather.
Electrolyte Imbalance
Electrolytes like potassium, calcium, and magnesium play a crucial role in muscle function. An imbalance in these minerals can lead to spasms. Low levels of potassium or calcium are particularly known to cause muscle cramps.
Overuse of Muscles
Overworking muscles during exercise or physical labor can lead to spasms. When muscles are fatigued, they are more likely to cramp. This is common among athletes or individuals who engage in repetitive motions.
Poor Blood Circulation
Inadequate blood flow to muscles can cause spasms. Conditions like peripheral artery disease can restrict blood flow, leading to cramping, especially in the legs.
Nerve Compression
Compressed nerves in the spine can cause muscle spasms. This is often seen in conditions like herniated discs or spinal stenosis. The spasms are usually accompanied by pain or numbness.
Medications
Certain medications can cause muscle spasms as a side effect. Diuretics, statins, and medications for high blood pressure are known to increase the risk of cramps.
Medical Conditions
Some medical conditions can lead to muscle spasms. These include diabetes, kidney disease, and thyroid disorders. Managing the underlying condition is key to reducing spasms.
Relief for Muscle Spasms
Finding relief from muscle spasms involves addressing the underlying cause and using techniques to relax the affected muscle.
Stretching and Massage
Gently stretching the affected muscle can help relieve a spasm. Massaging the area can also promote relaxation and reduce pain. For example, stretching the calf muscle by pulling the toes upward can alleviate a leg cramp.
Heat and Cold Therapy
Applying heat can relax tense muscles and improve blood flow. A warm towel or heating pad can be effective. Cold therapy, such as an ice pack, can reduce inflammation and numb the pain.
Hydration
Drinking plenty of fluids can prevent and relieve muscle spasms caused by dehydration. Water is the best choice, but electrolyte-rich drinks can also help restore balance.
Electrolyte Supplements
Taking supplements for potassium, calcium, or magnesium can address deficiencies that cause spasms. Consult a healthcare provider before starting any supplements.
Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers
Non-prescription pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can reduce pain and inflammation associated with muscle spasms. Use them as directed.
Rest
Giving the affected muscle time to rest and recover is essential. Avoid activities that strain the muscle until the spasm subsides.
Prevention Tips for Muscle Spasms
Preventing muscle spasms involves lifestyle changes and proactive measures to reduce risk factors.
Stay Hydrated
Drink enough water throughout the day, especially during physical activity. Aim for at least eight glasses of water daily. Increase intake during hot weather or intense exercise.
Maintain Electrolyte Balance
Include foods rich in potassium, calcium, and magnesium in your diet. Bananas, leafy greens, nuts, and dairy products are excellent sources. Avoid excessive consumption of salty or processed foods.
Warm-Up Before Exercise
Always warm up before engaging in physical activity. Stretching and light exercises prepare the muscles and reduce the risk of spasms.
Avoid Overexertion
Listen to your body and avoid pushing muscles beyond their limits. Take breaks during physical labor or exercise to prevent fatigue.
Improve Posture
Maintaining good posture can prevent nerve compression and reduce the risk of spasms. Use ergonomic furniture and practice proper body mechanics.
Regular Exercise
Engaging in regular physical activity strengthens muscles and improves circulation. Focus on exercises that promote flexibility and endurance.
Manage Medical Conditions
If you have a medical condition that contributes to muscle spasms, work with your healthcare provider to manage it effectively. Follow prescribed treatments and monitor symptoms.
Limit Caffeine and Alcohol
Excessive caffeine and alcohol can lead to dehydration and electrolyte imbalances. Limit consumption to reduce the risk of spasms.
Wear Proper Footwear
Wearing supportive shoes can prevent muscle strain, especially in the legs and feet. Avoid high heels or ill-fitting shoes for extended periods.
Practice Stress Management
Stress can contribute to muscle tension and spasms. Techniques like deep breathing, meditation, or yoga can help manage stress levels.
When to See a Doctor
Most muscle spasm is harmless and resolves on their own. However, consult a healthcare provider if you experience:
- Frequent or severe spasms
- Spasms that do not improve with self-care
- Swelling, redness, or warmth in the affected area
- Muscle weakness or loss of function
- Spasms accompanied by other concerning symptoms
A doctor can diagnose underlying conditions and recommend appropriate treatment.
Conclusion
Muscle spasms are common but can be managed effectively with the right approach. Understanding the causes, finding relief, and adopting prevention strategies can reduce their impact on daily life. Stay hydrated, maintain a balanced diet, and practice healthy habits to keep muscles functioning smoothly. If spasms persist or worsen, seek medical advice to address any underlying issues. Taking proactive steps can help you unlock the mystery of muscle spasms and enjoy a more comfortable, active life.