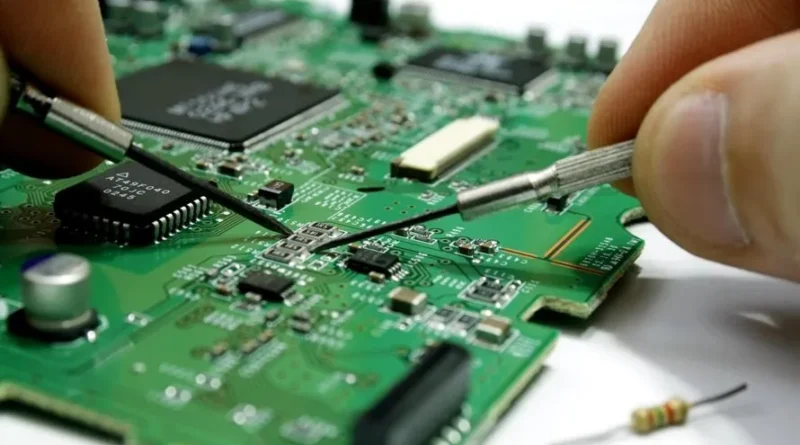
PCB Quality Check: Common Mistakes & Pick & Place Machines
Printed circuit boards (PCBs) are essential components in almost all electronic devices, from smartphones to computers. It is important to ensure the quality of these boards as even small errors can cause the devices to malfunction or fail. In this article, we’ll look at best practices for testing PCB quality, discuss common design mistakes to avoid, and explain how surface mount technology (SMT) pick and place machines are critical to the PCB assembly process.
PCB quality control methods
To ensure high-quality PCBs, manufacturers use several methods to check PCB quality control at every step. Here are some of the main methods:
Visual inspection
Visual inspection is the easiest way to check for obvious defects such as misaligned parts, soldering problems, or damaged areas. Although basic, this step is important to catch visible errors early.
Automated Optical Inspection (AOI)
AOI uses high-resolution cameras and software to automatically scan PCBs for defects. It compares the board to a standard model to quickly find problems such as missing parts, solder bridges, or incorrect placement. AOI helps ensure that only boards that meet strict standards advance to the next step.
X-ray inspection
X-ray inspection is great for finding hidden defects inside PCBs that you can’t see with the naked eye. It is especially useful for checking solder joints under chips that are not visible on the surface. This method helps detect problems such as voids, misalignments, and weak solder joints.
In-Circuit Testing (ICT)
In-circuit testing uses special equipment to check if the components on the PCB are working properly. It verifies that there are no open or short circuits and that the board functions as intended. ICT is highly effective in detecting assembly errors and ensuring proper functionality.
Functional testing
Functional testing tests how a PCB performs under real-world conditions by simulating its operating environment. This test ensures that all components work together properly. It is usually the final step before a PCB is approved for use in manufacturing.
Common PCB Design Mistakes to Avoid
Even if you have strong quality control procedures, PCB design mistakes can lead to serious problems. Here are some common design mistakes to avoid:
Not enough space between the components
Placing components too close together can cause electrical shorts and make assembly difficult. Always follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for spacing to avoid these problems.
Poor ground plane design
A ground plane helps reduce electrical noise and interference on the PCB. A poorly designed ground plane can cause signal problems and unpredictable behavior. Make sure your ground plane is solid and continuous with enough diameter to maintain good grounding.
Incorrect trace width
Traces that are too narrow cannot handle enough current and may overheat or fail. On the other hand, too wide traces waste precious space on the board. Use the trace width calculator to properly size the trace for the required current load.
Ignore thermal management
Components that generate a lot of heat need good thermal management to prevent overheating. If you don’t plan for heat dissipation, it can lead to performance problems and shorten the life of your PCB.
Overlooking Design for Manufacturability (DFM).
Designing for manufacturability means creating a PCB that is easy and cost-effective to manufacture. Common DFM mistakes include using non-standard component sizes, complex routing, and placing components too close to the edge of the board. Following the DFM guidelines helps create a more reliable and affordable board.
Role of SMT Pick and Place Machines in PCB Assembly
SMT pick and place machine in PCB assembly plays a crucial role in modern PCB assembly. These machines place surface-mount components on PCBs quickly and accurately. Here’s why they’re so important:
Accuracy and precision
SMT pick and place machines use an advanced vision system to perfectly align components with PCB pads. This precision is difficult to achieve manually, especially for boards with many small components.
Speed and efficiency
These machines can place thousands of components per hour, speeding up production and reducing the chance of human error. This functionality ensures consistent quality across the board.
Consistency in Legislature
Consistency is key in quality control. SMT Pick and Place machines operate under controlled conditions, ensuring that each component is placed exactly where it should be. This compatibility is important for boards that require high reliability.
Flexibility in production
Modern SMT pick and place machines can handle a wide range of component types and sizes, making them ideal for both small prototypes and large-scale production. Their flexibility gives manufacturers a variety of designs without sacrifice.