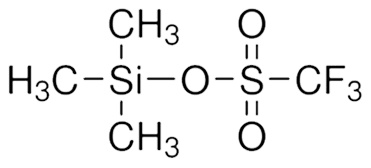
Trimethylsilyl Trifluoromethanesulfonate || CAS No : 27607-77-8 || Manufacturer || India
Trimethylsilyl trifluoromethanesulfonate, commonly known as TMSOTf, is a versatile reagent widely used in organic synthesis. This guide provides comprehensive information about TMSOTf, including its chemical properties, uses, mechanisms, handling precautions, and more.
What is Trimethylsilyl Trifluoromethanesulfonate?
Trimethylsilyl trifluoromethanesulfonate (TMSOTf) is a chemical compound used primarily as a silylating agent in organic chemistry. It is known for its ability to facilitate various reactions, including the protection of alcohols, nucleophilic substitutions, and the activation of electrophiles.
Chemical Properties
- Chemical Formula: C4H9F3O3SSi
- Case No:-27607-77-8
- Molecular Weight: 222.26 g/mol
- Appearance: Colorless to pale yellow liquid
- Boiling Point: 104°C (219.2°F)
- Density: 1.322 g/cm³ at 25°C
- Solubility: Soluble in many organic solvents, such as dichloromethane, toluene, and acetonitrile.
Manufacturer
TMSOTf is produced by several chemical manufacturers specializing in reagents for laboratory and industrial applications. These manufacturers ensure high purity and consistent quality through rigorous quality control measures.
Uses of Trimethylsilyl Trifluoromethanesulfonate
TMSOTf is employed in various synthetic applications:
- Silylation: It is commonly used to protect alcohols, amines, and other nucleophiles by converting them into their trimethylsilyl (TMS) derivatives.
- Activation of Electrophiles: It activates carbonyl compounds, imines, and other electrophiles, enhancing their reactivity in nucleophilic addition reactions.
- Catalysis: Acts as a catalyst in several organic transformations, including cyclization, rearrangement, and polymerization reactions.
- Formation of Silyl Enol Ethers: Used in the preparation of silyl enol ethers from ketones and aldehydes, which are useful intermediates in organic synthesis.
How Trimethylsilyl Trifluoromethanesulfonate Works
TMSOTf works by transferring a trimethylsilyl group to nucleophilic centers. The typical steps in a reaction involving TMSOTf include:
- Activation: TMSOTf reacts with a nucleophile (e.g., alcohol, amine) to form a trimethylsilyl-protected intermediate.
- Reaction: The silylated intermediate undergoes further reactions, such as nucleophilic substitution or elimination, to form the desired product.
- Deprotection: The trimethylsilyl group can be removed under acidic or basic conditions to regenerate the original functional group.
Handling and Storage
Proper handling and storage of TMSOTf are crucial due to its reactive nature:
- Storage: Store TMSOTf in a cool, dry place, preferably under an inert atmosphere such as nitrogen or argon. Keep it in tightly sealed containers away from moisture and light.
- Handling: Use appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including gloves, safety goggles, and lab coats. Work in a well-ventilated area or under a fume hood to avoid inhalation and contact with skin or eyes.
Precautions
When using TMSOTf, consider the following safety precautions:
- Health Hazards: TMSOTf is corrosive and can cause severe burns to the skin and eyes. Inhalation of vapors can cause respiratory irritation.
- Reactivity: It reacts violently with water, alcohols, and other nucleophiles, releasing toxic and corrosive fumes.
- Environmental Safety: Dispose of TMSOTf and its byproducts according to local environmental and safety regulations.
Side Effects and Toxicity
- Acute Exposure: Can cause severe skin and eye irritation or burns, and respiratory tract irritation if inhaled. Immediate medical attention is required in case of contact.
- Chronic Exposure: Prolonged or repeated exposure can lead to chronic respiratory issues and skin sensitization.
Applications in Research and Industry
- Pharmaceuticals: Used in the synthesis of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and intermediates.
- Material Science: Employed in the modification of materials to introduce silyl functionalities.
- Organic Synthesis: Integral in various organic transformations, including protection and deprotection strategies, cyclizations, and rearrangements.
FAQ
1. Can TMSOTf be used in aqueous solutions?
- No, TMSOTf reacts violently with water and should only be used in anhydrous conditions and non-aqueous solvents.
2. How should I dispose of TMSOTf?
- Dispose of TMSOTf according to local hazardous waste disposal regulations. Consult your institution’s safety guidelines for proper disposal methods.
3. What is the shelf life of TMSOTf?
- When stored properly under an inert atmosphere and away from moisture, TMSOTf can have a long shelf life. Check the manufacturer’s specifications for exact details.
4. Can TMSOTf be used with other reagents?
- Yes, TMSOTf can be used in combination with other reagents to facilitate complex organic transformations. However, care must be taken to avoid incompatible reactions.
5. Is TMSOTf compatible with all solvents?
- TMSOTf is soluble in many organic solvents such as dichloromethane, toluene, and acetonitrile, but it must be kept away from protic solvents like water and alcohols.
6. What should I do if TMSOTf comes into contact with my skin?
- Rinse the affected area with plenty of water and seek immediate medical attention.
Conclusion
Trimethylsilyl trifluoromethanesulfonate (TMSOTf) is a highly reactive and valuable reagent in organic chemistry, known for its ability to facilitate a wide range of chemical transformations. Its powerful silylating properties make it indispensable in the synthesis of pharmaceuticals, advanced materials, and various organic compounds. By understanding its properties, uses, and handling precautions, chemists can effectively and safely utilize TMSOTf in their research and industrial applications.