Understanding CNC Turning: A Comprehensive Guide to Precision Machining
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) turning has become a cornerstone of modern manufacturing due to its ability to produce high-precision, high-quality components. As industries continue to demand faster production times and greater accuracy, CNC turning is increasingly essential for meeting these needs. Whether in aerospace, automotive, medical, or consumer electronics, CNC turning machines are central to producing parts with exact specifications. This article will explore what CNC turning is, its advantages, common applications, and why it’s so crucial in the world of manufacturing.
What is CNC Turning?
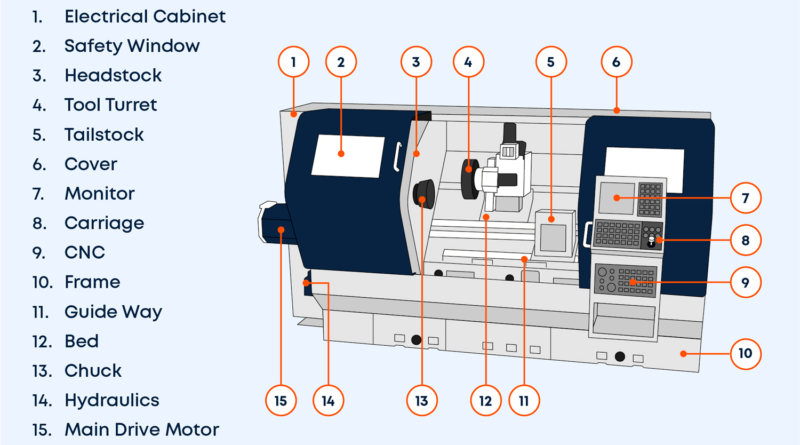
CNC turning is a machining process used to manufacture cylindrical parts by rotating the workpiece against a cutting tool that removes material. The operation is controlled by a computer program that defines the movement and operation of the machine. The machine is designed to rotate the material, often a rod or bar, while cutting tools are precisely guided along the workpiece to shape it according to the specifications.
Unlike traditional turning, which requires manual operation of the machine by an operator, CNC turning machines automate the process, increasing precision and reducing the risk of human error. The use of CNC technology allows for the production of highly detailed parts with tight tolerances, quickly and efficiently.
CNC Turning Process Overview
- Designing the Part: The first step in CNC turning involves creating a detailed digital design of the component using CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software. This design is then converted into machine-readable instructions using CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing) software.
- Setting Up the Machine: The workpiece is securely mounted on the CNC lathe machine, which rotates it at high speeds while the cutting tools move in precise paths.
- Cutting and Shaping: The cutting tool removes material from the rotating workpiece according to the specifications defined in the CNC program. Various operations such as turning, facing, drilling, and threading can be done on the workpiece.
- Finishing: After the machining process, parts may undergo additional steps like polishing or coating to meet the required finish or performance criteria.
Key Advantages of CNC Turning
CNC turning machines offer several key benefits, making them a popular choice in various industries. Here are some of the advantages that have made CNC turning a widely adopted manufacturing technique:
1. High Precision and Accuracy
One of the standout features of CNC turning is its ability to produce parts with extremely tight tolerances. CNC machines can achieve levels of precision that are often impossible to achieve with manual turning. This is especially important in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and medical, where parts must adhere to strict specifications.
2. Increased Production Speed
Once a CNC turning machine is set up, it can run continuously without the need for manual intervention, leading to faster production times. This is particularly advantageous in mass production, where high-volume manufacturing is required. The automated process ensures that parts can be produced at a quicker pace without sacrificing accuracy.
3. Consistency and Repeatability
After the initial setup, CNC turning machines can produce identical parts with the same high level of accuracy every time. This repeatability is crucial in industries that require large quantities of the same part, as it ensures that each piece meets the same standards, reducing the need for rework and minimizing waste.
4. Versatility in Part Design
CNC turning is capable of producing a wide variety of parts with complex geometries, including shafts, rings, and components with threads, grooves, or other detailed features. The machine can also handle a range of materials, from metals like steel, aluminum, and titanium to plastics and composites, making it suitable for a diverse set of applications.
5. Reduced Human Error
Traditional turning processes can be prone to mistakes due to human error, such as incorrect measurements or improper machine settings. With CNC turning, the process is automated and controlled by computer programming, reducing the likelihood of errors and ensuring consistent results across multiple production runs.
6. Cost-Effectiveness for Mass Production
CNC turning is particularly cost-effective for high-volume production runs. While the initial setup cost of a CNC machine may be higher than traditional machines, the reduced labor costs, speed of production, and consistent results lead to lower costs in the long term.
Common CNC Turning Operations
CNC turning machines can perform a variety of operations depending on the part being produced. Below are some common operations that are often used in CNC turning:
1. Facing
Facing is the process of machining the flat surface at the end of the workpiece. It is typically one of the first operations performed on a workpiece to create a smooth, level surface for subsequent operations.
2. Turning
Turning involves removing material from the outside diameter of the workpiece to reduce its size or shape it into a cylindrical form. This is the most basic and common operation in CNC turning.
3. Drilling and Boring
Drilling is the process of creating holes in the workpiece, while boring is used to enlarge and finish existing holes. Both operations are commonly performed on CNC turning machines to create precise internal features.
4. Threading
CNC turning machines can create both internal and external threads on workpieces, making them ideal for producing fasteners, bolts, and other threaded components.
5. Grooving and Cut-Off
Grooving is the process of creating grooves or channels on the surface of the workpiece. The cut-off operation removes parts from the workpiece, creating separate components or removing excess material.
Applications of CNC Turning
CNC turning machines are used across a wide range of industries to create various types of cylindrical and complex parts. Here are some of the common applications of CNC turning:
1. Aerospace Industry
The aerospace industry demands parts that can withstand high stresses, extreme temperatures, and other harsh conditions. CNC turning is used to produce critical components such as turbine blades, engine shafts, and other precision-engineered parts for aircraft and spacecraft.
2. Automotive Industry
CNC turning plays a vital role in the automotive sector, where high-quality, precision-engineered parts are required for performance and safety. CNC turning machines are used to manufacture components like gears, camshafts, brake discs, and pistons that are essential for the functionality of vehicles.
3. Medical Devices
The medical industry relies on CNC turning for the production of precision medical components such as surgical instruments, implants, and prosthetics. These parts often have intricate designs and must meet stringent safety standards, which CNC turning is perfectly suited for.
4. Oil and Gas
In the oil and gas industry, parts that need to operate in extreme conditions, such as valves, flanges, and pipes, are often produced using CNC turning. CNC turning machines can create durable, precise components that meet the demands of high-pressure and high-temperature environments.
5. Consumer Electronics
CNC turning is widely used in the production of components for consumer electronics. From smartphone casings to connectors, CNC turning ensures that the parts are precisely manufactured to fit together seamlessly, ensuring the high functionality and aesthetic appeal of electronic devices.
6. Defense Industry
The defense industry requires parts that can perform under demanding conditions, and CNC turning is often used to create high-precision components for military vehicles, weapons systems, and communication equipment. The accuracy and repeatability of CNC turning make it a critical technology in defense manufacturing.
Industries That Benefit from CNC Turning
A wide range of industries rely on CNC turning for its precision, speed, and versatility. These industries include:
- Aerospace: Manufacturing components like turbine blades, brackets, and actuators.
- Automotive: Producing parts like gears, camshafts, and brake components.
- Medical: Creating surgical tools, implants, and diagnostic devices.
- Oil and Gas: Fabricating high-strength components for drilling, pipelines, and valves.
- Electronics: Producing casings and connectors for consumer gadgets.
- Defense: Producing components for weapons, military vehicles, and defense systems.
Conclusion
CNC turning has transformed manufacturing by enabling the precise and efficient production of complex parts. Its high level of accuracy, speed, and repeatability makes it indispensable in industries that require precision-engineered components. Whether it’s in the aerospace, automotive, medical, or electronics sector, CNC turning provides the flexibility to produce parts from a wide range of materials while meeting demanding tolerances and performance standards. As technology continues to advance, CNC turning will remain a central part of the modern manufacturing landscape, helping industries produce high-quality, cost-effective components at scale.