Managing Acute Musculoskeletal Pain Effectively
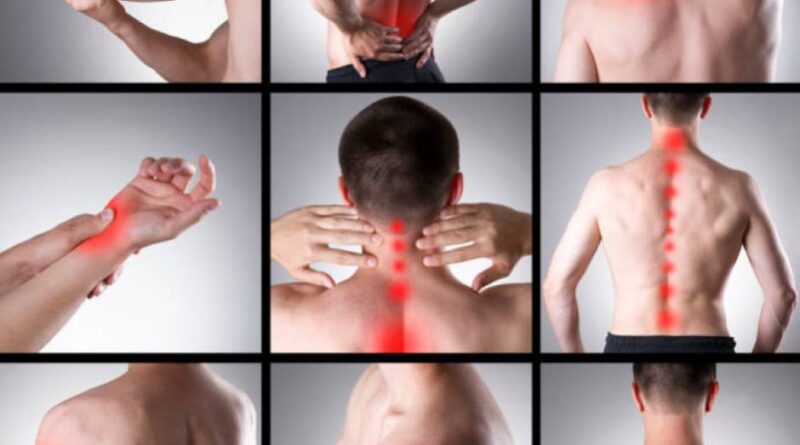
Acute musculoskeletal pain is a common condition that affects millions of individuals worldwide. It can result from injuries, overuse, or medical conditions such as arthritis or sprains. Proper management is essential for ensuring swift recovery and preventing chronic pain. This article provides a comprehensive guide to understanding, treating, and preventing acute musculoskeletal pain effectively.
Understanding Acute Musculoskeletal Pain
Musculoskeletal pain refers to discomfort affecting the muscles, bones, ligaments, tendons, or nerves. Acute pain is typically short-term, lasting less than three months, and is often caused by trauma or strain. Common causes include:
- Sprains and Strains: Overstretching or tearing of ligaments and muscles.
- Fractures: Breaks in the bones due to impact or stress.
- Tendinitis: Inflammation of tendons due to repetitive motion.
- Bursitis: Swelling of fluid-filled sacs that cushion joints.
- Overuse Injuries: Resulting from excessive physical activity without adequate rest.
Medical Treatment
Prescription Medication
Some prescription medications are designed to support musculoskeletal health by addressing pain and discomfort associated with muscle conditions. Healthcare providers prescribe these medications based on individual needs and medical history.
One example is Pain O Soma 500mg, which is commonly used to manage acute muscle pain and discomfort. It works as a muscle relaxant, helping to relieve pain by blocking pain signals between the nerves and the brain. Recommended for individuals experiencing muscle spasms, injuries, or musculoskeletal disorders, Pain O Soma 500mg promotes relief and improved mobility, allowing users to regain comfort and enhance their daily activities.
Effective Treatment Strategies
1. Immediate First Aid
Applying immediate first aid can significantly reduce pain and prevent further injury. The R.I.C.E. method is a widely recommended approach:
- Rest: Avoid using the injured area to prevent worsening the condition.
- Ice: Apply ice packs for 15-20 minutes every few hours to reduce swelling.
- Compression: Use an elastic bandage to limit movement and swelling.
- Elevation: Keep the affected area raised to decrease blood flow and inflammation.
2. Medications for Pain Relief
Over-the-counter (OTC) and prescription medications play a vital role in pain management. Common options include:
- Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): Ibuprofen and naproxen help reduce inflammation and pain.
- Acetaminophen: Effective for mild to moderate pain relief.
- Topical Analgesics: Gels, creams, or patches containing menthol or capsaicin can provide localized relief.
- Muscle Relaxants: Prescribed for severe muscle spasms and discomfort.
3. Physical Therapy and Exercise
Rehabilitation through physical therapy enhances recovery by strengthening muscles and improving flexibility. Key exercises include:
- Stretching: Prevents stiffness and promotes mobility.
- Strength Training: Builds muscle support around joints to prevent re-injury.
- Low-Impact Activities: Swimming, yoga, and cycling help maintain movement without excessive strain.
4. Alternative Therapies
Many individuals find relief through alternative and complementary therapies, such as:
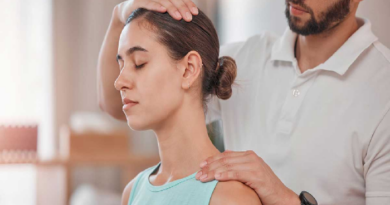
- Massage Therapy: Enhances blood circulation and reduces muscle tension.
- Acupuncture: Uses fine needles to stimulate natural pain relief mechanisms.
- Chiropractic Care: Aligns the spine and joints to improve function and reduce discomfort.
5. Lifestyle Modifications
Preventing recurrent acute musculoskeletal pain requires long-term lifestyle changes, including:
- Proper Posture: Maintaining correct body alignment to reduce stress on muscles and joints.
- Ergonomic Adjustments: Using supportive chairs, keyboards, and workstations.
- Balanced Diet: Consuming nutrients essential for bone and muscle health, such as calcium, vitamin D, and protein.
- Hydration: Keeping muscles and joints lubricated to prevent stiffness.
6. Medical Interventions
In severe cases, medical procedures may be necessary:
- Injections: Corticosteroid injections can provide temporary relief for inflammation.
- Surgical Intervention: Reserved for fractures, torn ligaments, or severe structural damage.
- Pain Management Programs: Multidisciplinary approaches combining medication, therapy, and counseling for long-term relief.
Preventing Acute Musculoskeletal Pain
Prevention is key to avoiding acute musculoskeletal pain. Essential preventive measures include:
- Warm-Up and Cool-Down: Stretch before and after physical activities.
- Gradual Progression: Increase activity levels gradually to avoid overuse injuries.
- Proper Footwear: Wear supportive shoes to prevent strain on the legs and back.
- Regular Exercise: Engage in routine strengthening and flexibility workouts.
Conclusion
Managing acute musculoskeletal pain effectively requires a multi-faceted approach that includes first aid, medication, therapy, and lifestyle changes. By understanding the causes, treatment options, and preventive measures, individuals can recover quickly and reduce the risk of chronic pain. Always consult a healthcare professional for personalized treatment strategies to ensure optimal recovery and well-being.